Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 observation of surface reactions; Present status and future prospects"
observation of surface reactions; Present status and future prospects"Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Hoshako, 35(3), P. 157, 2022/05
Ambient Pressure-XPS [AP-XPS] has been in operation at synchrotron radiation facilities around the world since around 2000 to study gas-surface reactions. Furthermore, it is also applied to observe liquid and solid-liquid interfaces. Development and utilization research is underway as a tool to take the true picture of surface phenomena. A special issue on AP-XPS for the Journal of the Japanese Society for Synchrotron Radiation Research was designed and its purpose is explained.
Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Matoba, Tomoki*; Koyama, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Yuki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Langmuir, 38(8), p.2642 - 2650, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)0xidation processes at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). The oxidation starts at the outermost Hf layers and produces stoichiometric HfO . Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si configuration) were generated in the vicinity of the HfO
. Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si configuration) were generated in the vicinity of the HfO /Si interface in the case of the irradiation of 2.2 eV SOMB. The oxidation of the Si substrate takes place to generate SiO
/Si interface in the case of the irradiation of 2.2 eV SOMB. The oxidation of the Si substrate takes place to generate SiO compounds. Si atoms were emitted from the SiO
compounds. Si atoms were emitted from the SiO /Si interface region underneath the HfO
/Si interface region underneath the HfO overlayers to release the stress generated within the strained Si layers. The emitted Si atoms can pass through the HfO
overlayers to release the stress generated within the strained Si layers. The emitted Si atoms can pass through the HfO overlayers and react with the impinging O
overlayers and react with the impinging O gas.
gas.
 O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Zhang, B.*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(5), p.218 - 223, 2021/05
The oxidation reaction kinetics on Ti(0001) and Ni(111) surfaces were observed by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation to measure the oxidation state and oxide thickness. After the Ti(0001) surface was wholly covered by TiO with a thickness of 1.2 nm, the rapid growth of n-type TiO proceeded through the diffusion of Ti
proceeded through the diffusion of Ti ions to the TiO
ions to the TiO surface at 400
surface at 400 C. A saturation of oxygen uptake on the TiO surface indicates that the O
C. A saturation of oxygen uptake on the TiO surface indicates that the O sticking coefficient on the TiO surface is negligibly small and the segregation of Ti to the TiO surface is a trigger to initiate the TiO
sticking coefficient on the TiO surface is negligibly small and the segregation of Ti to the TiO surface is a trigger to initiate the TiO growth. On the Ni(111) surface at 350
growth. On the Ni(111) surface at 350 C, a thermally stable NiO
C, a thermally stable NiO proceeded preferentially and then the growth of p-type NiO was initiated. The time evolution of NiO thickness was represented by a logarithmic growth model, where the NiO growth is governed by the electron tunneling to the NiO surface.
proceeded preferentially and then the growth of p-type NiO was initiated. The time evolution of NiO thickness was represented by a logarithmic growth model, where the NiO growth is governed by the electron tunneling to the NiO surface.
Doi, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Surface and Interface Analysis, 52(12), p.1117 - 1121, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.52(Chemistry, Physical)Ni-base alloys has been widely used for chemical plants because of their high strength and excellent oxidation resistance. In particular, the addition of Sn and Sb in Ni-base alloys significantly improves the metal dusting resistance. It is indicated that Sn and Sb are segregated on the alloy surface in the metal dusting environment; however, the details have not been clarified yet. The behavior of the Ni-Sn and Ni-Sb alloys under a high-temperature oxidation environment was investigated by in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was confirmed that Sn and Sb have been segregated at the surface of their alloys during oxidation in low oxygen potential environment. These results indicate that Sn and Sb segregation improves the metal dusting resistance.
 optical microscopy of crystal growth of graphene using thermal radiation
optical microscopy of crystal growth of graphene using thermal radiationTerasawa, Tomoo; Taira, Takanobu*; Obata, Seiji*; Saiki, Koichiro*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
Vacuum and Surface Science, 62(10), p.629 - 634, 2019/10
Graphene, an atomically thin sheet composed of sp carbon atoms, has been the most attractive material in this decade. The fascinating properties of graphene are exhibited when it is monolayer. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is widely used to produce monolayer graphene selectively in large-area. Here we introduce "radiation-mode optical microscopy" which we have developed in order to realize the
carbon atoms, has been the most attractive material in this decade. The fascinating properties of graphene are exhibited when it is monolayer. Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is widely used to produce monolayer graphene selectively in large-area. Here we introduce "radiation-mode optical microscopy" which we have developed in order to realize the  observation of the CVD growth of graphene. We show the method to observe graphene as bright contrast on Cu substrates in thermal radiation images. The growth mechanism, the nucleation site and rate limiting process, revealed by the
observation of the CVD growth of graphene. We show the method to observe graphene as bright contrast on Cu substrates in thermal radiation images. The growth mechanism, the nucleation site and rate limiting process, revealed by the  observation is presented. Finally, we show the CVD growth of graphene on Au substrates, resulting in the tuning of the emissivity of graphene by the pre-treatment procedures. Our method is not only a way to observe the graphene growth but also shed light on the thermal radiation property of graphene.
observation is presented. Finally, we show the CVD growth of graphene on Au substrates, resulting in the tuning of the emissivity of graphene by the pre-treatment procedures. Our method is not only a way to observe the graphene growth but also shed light on the thermal radiation property of graphene.
Terasawa, Tomoo; Taira, Takanobu*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Obata, Seiji*; Saiki, Koichiro*; Asaoka, Hidehito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 58(SI), p.SIIB17_1 - SIIB17_6, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.91(Physics, Applied)Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on substrates with low C solubility such as Cu and Au is promising to grow monolayer graphene selectively in a large scale. Hydrogen is often added to control the domain size of graphene on Cu, while Au does not require H since Ar is inert against oxidation. The effect of H
since Ar is inert against oxidation. The effect of H should be revealed to improve the quality of graphene on Au. Here we report the effect of H
should be revealed to improve the quality of graphene on Au. Here we report the effect of H on the CVD growth of graphene on Au substrates using in situ radiation-mode optical microscopy. The in situ observation and ex situ Raman spectroscopy revealed that whether H
on the CVD growth of graphene on Au substrates using in situ radiation-mode optical microscopy. The in situ observation and ex situ Raman spectroscopy revealed that whether H was supplied or not strongly affected the growth rate, thermal radiation contrast, and compressive strain of graphene on Au. We attributed these features to the surface reconstruction of Au(001) depending on H
was supplied or not strongly affected the growth rate, thermal radiation contrast, and compressive strain of graphene on Au. We attributed these features to the surface reconstruction of Au(001) depending on H supply. Our results are essential to achieve the graphene growth with high quality on Au for future applications.
supply. Our results are essential to achieve the graphene growth with high quality on Au for future applications.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako, 32(4), p.185 - 198, 2019/07
Synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy is a beneficial technique for precise analysis of chemical states of solid surfaces. Owing to its high luminosity, it ensures availability of termed synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy which enables " " observation of chemical reactions with gas molecules occurring at surfaces. In this review, oxygen adsorption reactions in the oxidation of silicon single crystal surfaces are focused. Through the demonstration of our research, the usefulness of synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to study molecular adsorption reactions at solid surfaces is briefly described and the future perspective would also be shown.
" observation of chemical reactions with gas molecules occurring at surfaces. In this review, oxygen adsorption reactions in the oxidation of silicon single crystal surfaces are focused. Through the demonstration of our research, the usefulness of synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy to study molecular adsorption reactions at solid surfaces is briefly described and the future perspective would also be shown.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 62(6), p.350 - 355, 2019/06
Thermal oxidation of Si substrate is an indispensable process for the Si device fabrication. However, the influence of oxidation induced strain cannot be ignored for thin films. Synchrotron radiation real-time photoelectron spectroscopy was used as a method to measure simultaneously oxidation induced strain and oxidation rate. It was found that the acceleration of interfacial oxidation induced by thermal strain was observed for the rapid thermal oxidation. The results can be explained by the model in which point defects caused by strain become reaction sites at the SiO /Si interface.
/Si interface.
Terasawa, Tomoo; Saiki, Koichiro*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
Dai-39-Kai Nihon Netsu Bussei Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (CD-ROM), p.262 - 264, 2018/11
Graphene, monolayer graphite, has been expected as one of the new materials targeting the next generation electronics since its first isolation in 2004, due to the ultrahigh carrier mobility up to 100,000 cm /Vs and high transparency of 97.7%. The high transparency of graphene make it invisible on various substrates. Particularly, graphene on Cu, one of the common growth substrates for high-quality graphene, cannot be observed by optical microscopes. Here, we report the optical microscopic method to visualize graphene using thermal radiation. We observed a Cu surface by a zoom-lens and a CMOS camera during the growth of graphene by chemical vapor deposition. When graphene was grown on Cu substrates, the thermal radiation intensity increased at the area covered with graphene. The thermal radiation contrast between Cu surfaces with and without graphene showed that the thermal radiation intensity increased as the number of graphene layers in a layer-by-layer manner. We quantitatively analyzed the thermal radiation contrasts at various temperatures. We found the thermal radiation contrast was independent from the sample temperature. This result suggests that the emissivity of graphene is independent from the temperature, which is consistent with the theory of the optical properties of graphene. Our findings are essential for the discussion of the thermal radiation from the atomically thin materials including graphene.
/Vs and high transparency of 97.7%. The high transparency of graphene make it invisible on various substrates. Particularly, graphene on Cu, one of the common growth substrates for high-quality graphene, cannot be observed by optical microscopes. Here, we report the optical microscopic method to visualize graphene using thermal radiation. We observed a Cu surface by a zoom-lens and a CMOS camera during the growth of graphene by chemical vapor deposition. When graphene was grown on Cu substrates, the thermal radiation intensity increased at the area covered with graphene. The thermal radiation contrast between Cu surfaces with and without graphene showed that the thermal radiation intensity increased as the number of graphene layers in a layer-by-layer manner. We quantitatively analyzed the thermal radiation contrasts at various temperatures. We found the thermal radiation contrast was independent from the sample temperature. This result suggests that the emissivity of graphene is independent from the temperature, which is consistent with the theory of the optical properties of graphene. Our findings are essential for the discussion of the thermal radiation from the atomically thin materials including graphene.
Wang, H.*; Idobe, Jin*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yoshikawa, Hirofumi*
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 22(7), p.2067 - 2071, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:40.22(Electrochemistry) synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy study of the oxidation of the Ge(100)-2
synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy study of the oxidation of the Ge(100)-2 1 surface by supersonic molecular oxygen beams
1 surface by supersonic molecular oxygen beamsYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Okada, Ryuta; Yamada, Yoichi*; Sasaki, Masahiro*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 141(17), p.174708_1 - 174708_7, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:29.76(Chemistry, Physical)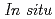 synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy was performed during the oxidation of the Ge(100)-2
synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy was performed during the oxidation of the Ge(100)-2 1 surface induced by a molecular oxygen beam with various incident energies up to 2.2 eV from the initial to saturation coverage of surface oxides. The saturation coverage of oxygen on the clean Ge(100) surface was much lower than one monolayer and the oxidation state of Ge was +2 at most. This indicates that the Ge(100) surface is in strong contrast to Si surfaces. The direct adsorption process can be activated by increasing the translational energy, resulting in an increased population of Ge
1 surface induced by a molecular oxygen beam with various incident energies up to 2.2 eV from the initial to saturation coverage of surface oxides. The saturation coverage of oxygen on the clean Ge(100) surface was much lower than one monolayer and the oxidation state of Ge was +2 at most. This indicates that the Ge(100) surface is in strong contrast to Si surfaces. The direct adsorption process can be activated by increasing the translational energy, resulting in an increased population of Ge and a higher final oxygen coverage. Our findings will contribute to the fundamental understanding of oxygen adsorption processes at 300 K from the initial stages to saturated oxidation.
and a higher final oxygen coverage. Our findings will contribute to the fundamental understanding of oxygen adsorption processes at 300 K from the initial stages to saturated oxidation.

Fuchizaki, Kazuhiro*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Omura, Ayako*; Hamaya, Nozomu*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Okada, Taku
Journal of Chemical Physics, 120(23), p.11196 - 11199, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:58.21(Chemistry, Physical)The location of the liquidus in the low-pressure crystalline phase of SnI was determined utilizing
was determined utilizing  X-ray diffraction measurements under pressures up to approximately
X-ray diffraction measurements under pressures up to approximately 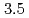 GPa. The liquidus is not well fitted to a monotonically increasing curve such as Simon's equation, but breaks near
GPa. The liquidus is not well fitted to a monotonically increasing curve such as Simon's equation, but breaks near  GPa and then becomes almost flat. The results are compared to those from molecular dynamics simulations. Ways to improve the model potential adopted in the simulations are discussed.
GPa and then becomes almost flat. The results are compared to those from molecular dynamics simulations. Ways to improve the model potential adopted in the simulations are discussed.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden; Moritani, Kosuke; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Mizuno, Yoshiyuki*; Tonda, Hideki*; Homma, Teiichi*
Shinku, 47(6), p.457 - 461, 2004/06
The oxidation reaction of Ti(0001) surface by oxygen molecules was observed by real-time in-situ photoemission spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation in the conditions of 400 C and 3.7
C and 3.7 10
10 Pa. The uptake curve of oxygen showed a plateau at the dose of 45-85 L and then increased again. This re-growth of oxide film was attributed to the drastic change of Ti oxidation state from TiO to TiO
Pa. The uptake curve of oxygen showed a plateau at the dose of 45-85 L and then increased again. This re-growth of oxide film was attributed to the drastic change of Ti oxidation state from TiO to TiO . Consequently, the characteristic change of the uptake curve was caused by the oxidation state change of Ti atoms.
. Consequently, the characteristic change of the uptake curve was caused by the oxidation state change of Ti atoms.
 Si-
Si-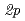 core-level spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation for Si(001) initial oxidation by translational kinetic energy of O
core-level spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation for Si(001) initial oxidation by translational kinetic energy of O molecules
moleculesYoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 26(2), p.755 - 758, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Katayama, Yoshinori
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 8(Part2), p.182 - 185, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Miura, Takayuki*; Kuwano, Hisashi*; Kikuchi, Kenji
Tetsu To Hagane, 87(2), p.31 - 36, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Abe, Hiroaki
Tanso Sogenryo Kagaku To Zairyo Sekkei, 3, p.5 - 14, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Ono, K.*; Arakawa, Kazuto*; Ohashi, Masahiro*; Kurata, Hiroki; Hojo, Kiichi; Yoshida, Naoaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 283-287(Part.1), p.210 - 214, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Aruga, Takeo; Katano, Yoshio*
Proceedings of 2000 International Conference on Ion Implantation Technology (IIT 2000), p.797 - 800, 2000/00
no abstracts in English